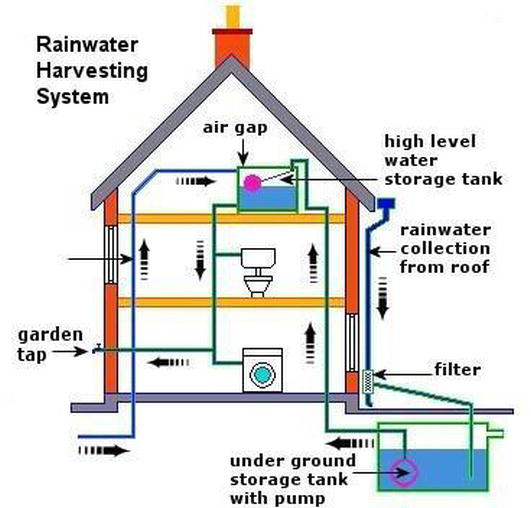
How Farmers Use Rainwater Harvesting for Crops

Rainwater harvesting is an ancient yet increasingly vital practice that farmers around the world use to sustainably manage water resources for crop irrigation. By capturing and storing rainwater, farmers can reduce dependency on groundwater and municipal water supplies, improve crop yields, and promote environmental conservation.
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops, land surfaces, or rock catchments using simple to complex systems. This water is then used for irrigation, livestock, and sometimes even for domestic purposes.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting Used by Farmers
| Method | Description | Advantages | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Runoff Harvesting | Collecting rainwater from fields or catchment areas into ponds or reservoirs | Low cost, easy to implement | Supplementing irrigation during dry spells |
| Roof Water Harvesting | Capturing rainwater from building rooftops into storage tanks | Clean water source, reduces soil erosion | Small-scale irrigation and household use |
| Check Dams | Small barriers built across streams to slow water flow and increase infiltration | Recharges groundwater, controls erosion | Enhancing soil moisture for nearby crops |
| Contour Bunding | Creating embankments along contour lines to capture runoff | Prevents soil erosion, improves water retention | Hilly or sloped farmland irrigation |
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting for Crops
- Water Conservation: Reduces reliance on groundwater and surface water.
- Cost-Effective: Lowers irrigation costs by utilizing free rainwater.
- Improved Crop Yields: Ensures water availability during dry periods.
- Soil Health: Prevents erosion and maintains soil moisture.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces flooding and groundwater depletion.
Step-by-Step Guide for Farmers to Implement Rainwater Harvesting
- Assess Rainfall Patterns: Understand local rainfall frequency and intensity.
- Select Appropriate Harvesting Method: Choose based on farm size, topography, and crop type.
- Design Storage Systems: Build ponds, tanks, or check dams suited to water volume.
- Install Conveyance Structures: Gutters, pipes, or channels to direct water.
- Maintain Systems Regularly: Clean storage tanks and repair structures to ensure efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can rainwater harvesting be used in areas with low rainfall?
A1: Yes, even small amounts of rain can be collected and stored efficiently to support crops during dry spells.
Q2: What crops benefit most from rainwater harvesting?
A2: Most crops benefit, especially those sensitive to water stress like vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
Q3: Is rainwater harvesting expensive to set up?
A3: Costs vary, but many methods are low-cost and can be implemented with local materials.
Q4: How does rainwater harvesting affect soil quality?
A4: It helps maintain soil moisture and reduces erosion, improving overall soil health.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable, cost-effective strategy that empowers farmers to manage water resources efficiently, improve crop productivity, and contribute to environmental conservation. By adopting suitable harvesting techniques, farmers can secure their livelihoods against the challenges of water scarcity and climate variability.