Wastewater Treatment in Rural Areas: Challenges

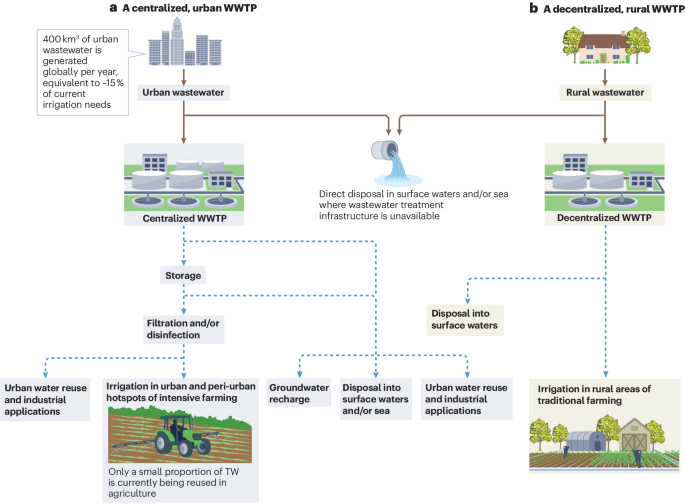
Wastewater treatment in rural areas presents unique challenges that differ significantly from urban settings. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective and sustainable solutions.
Key Challenges
1. Limited Infrastructure
Rural areas often lack the necessary infrastructure for efficient wastewater collection and treatment. This includes insufficient sewage networks, treatment plants, and maintenance facilities.
2. Financial Constraints
Budget limitations in rural communities can hinder the development and upkeep of wastewater treatment systems. Funding is often scarce, and prioritizing wastewater management competes with other essential services.
3. Geographic and Demographic Factors
Rural regions may be spread out with low population density, making centralized treatment systems less feasible. The terrain can also pose difficulties for infrastructure development.
4. Technical Expertise
There is often a shortage of trained personnel to operate and maintain wastewater treatment facilities in rural areas, leading to operational inefficiencies.
5. Environmental Impact
Improperly treated wastewater can contaminate local water bodies, affecting ecosystems and public health. Rural areas may lack monitoring and enforcement mechanisms.
Solutions and Strategies
| Challenge | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|
| Limited Infrastructure | Decentralized treatment systems, constructed wetlands |
| Financial Constraints | Government grants, community funding, low-cost technologies |
| Geographic Factors | Modular and mobile treatment units |
| Technical Expertise | Training programs, remote monitoring |
| Environmental Impact | Regular monitoring, community awareness campaigns |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is wastewater treatment important in rural areas?
A1: It protects public health, preserves the environment, and supports sustainable development.
Q2: What are common wastewater treatment methods suitable for rural areas?
A2: Methods include septic tanks, constructed wetlands, and small-scale biological treatment systems.
Q3: How can rural communities overcome financial challenges?
A3: Through government subsidies, partnerships with NGOs, and adopting cost-effective technologies.
Q4: What role does community involvement play?
A4: Community engagement ensures better maintenance, awareness, and sustainability of wastewater systems.
By addressing these challenges with tailored solutions, rural areas can improve wastewater management, safeguarding health and the environment.