Common Myths About Wastewater Treatment
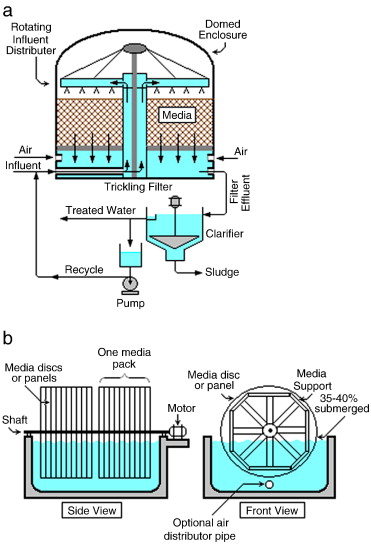
Wastewater treatment is a critical process for maintaining public health and protecting the environment. However, many misconceptions surround this essential service. In this article, we will debunk some of the most common myths about wastewater treatment, providing clear and accurate information.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Wastewater Treatment
- Common Myths and Facts
- Importance of Wastewater Treatment
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Introduction to Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment involves the removal of contaminants from water that has been used in homes, industries, and businesses. The goal is to produce water that is safe to return to the environment or reuse. Treatment processes typically include physical, chemical, and biological methods.
2. Common Myths and Facts
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Wastewater treatment plants only treat sewage. | They also treat industrial wastewater and stormwater runoff. |
| Treated wastewater is unsafe for reuse. | Properly treated wastewater meets strict safety standards and can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and even replenishing groundwater. |
| Wastewater treatment is harmful to the environment. | Modern treatment plants use eco-friendly technologies that minimize environmental impact. |
| All wastewater is treated the same way. | Treatment varies depending on the source and contaminants present. |
| Wastewater treatment is too expensive to maintain. | Investing in treatment saves money in the long term by preventing pollution and health issues. |
3. Importance of Wastewater Treatment
- Protects Public Health: Removes harmful pathogens and pollutants.
- Preserves Ecosystems: Prevents contamination of rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- Supports Water Reuse: Helps conserve freshwater resources.
- Complies with Regulations: Ensures communities meet environmental laws.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can treated wastewater be used for drinking?
A1: While treated wastewater is generally not used directly for drinking, advanced treatment technologies can make it safe for potable reuse in some cases.
Q2: Does wastewater treatment produce harmful byproducts?
A2: Treatment processes are designed to minimize harmful byproducts, and any residuals are managed safely.
Q3: How often should wastewater treatment plants be maintained?
A3: Regular maintenance is essential and typically occurs daily, with more extensive checks monthly or annually.
Q4: Is wastewater treatment energy-intensive?
A4: It can be, but many plants are adopting energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources.
By understanding the facts behind these common myths, we can better appreciate the vital role wastewater treatment plays in our communities and the environment.
