Why Wastewater Treatment Is Crucial for Health
Wastewater treatment plays a vital role in protecting public health and the environment. Proper treatment of wastewater ensures that harmful contaminants and pathogens are removed before water is released back into natural water bodies or reused. This article explores the importance of wastewater treatment, its benefits, and how it safeguards human health.
What Is Wastewater Treatment?
Wastewater treatment is the process of removing pollutants from water that has been used in homes, industries, and agriculture. This water contains organic matter, chemicals, and microorganisms that can be harmful if not treated properly.
Why Is Wastewater Treatment Important for Health?
- Prevents Waterborne Diseases: Untreated wastewater can carry bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid.
- Protects Drinking Water Sources: Proper treatment prevents contamination of rivers, lakes, and groundwater, which are sources of drinking water.
- Reduces Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Industrial wastewater may contain hazardous chemicals that can cause long-term health issues.
- Prevents Environmental Pollution: Treated wastewater reduces the risk of pollution that can affect food chains and ecosystems.
The Wastewater Treatment Process
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Preliminary | Removal of large solids and debris |
| Primary | Sedimentation to remove suspended solids |
| Secondary | Biological treatment to degrade organic matter |
| Tertiary | Advanced treatment to remove nutrients and pathogens |
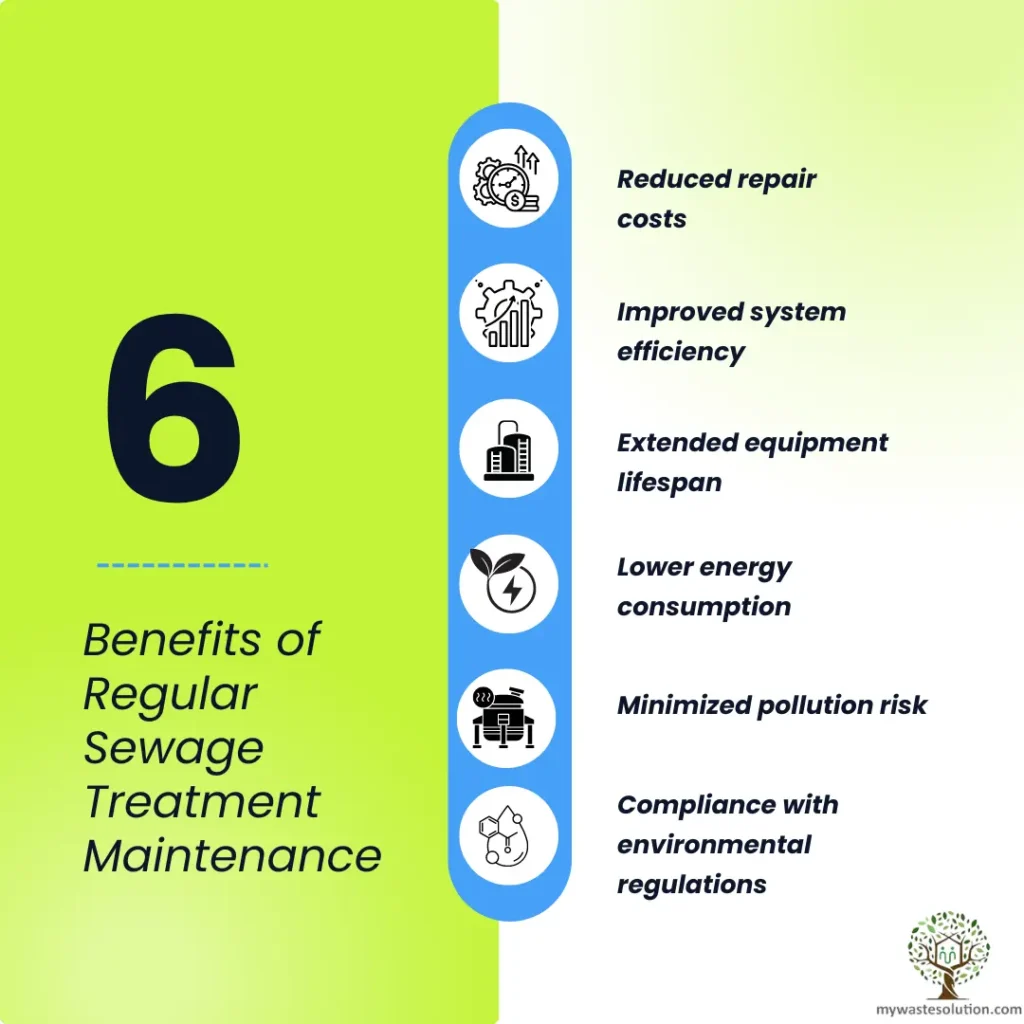
Benefits of Wastewater Treatment
- Improves Public Health: Reduces disease outbreaks.
- Protects Ecosystems: Maintains biodiversity and water quality.
- Supports Sustainable Water Use: Enables water recycling and reuse.
- Economic Benefits: Reduces healthcare costs and supports industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
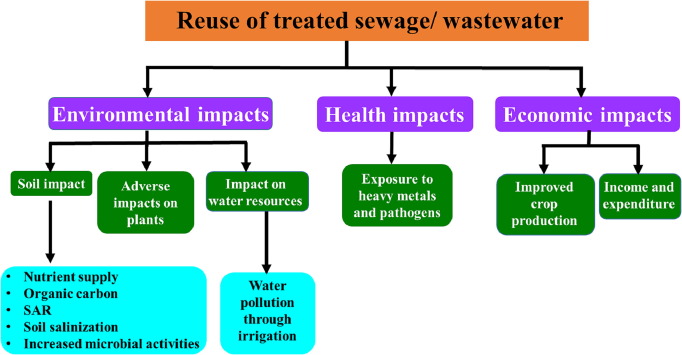
Q1: Can treated wastewater be reused safely?
A1: Yes, treated wastewater can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and even replenishing groundwater, provided it meets safety standards.
Q2: What happens if wastewater is not treated?
A2: Untreated wastewater can contaminate drinking water, spread diseases, and harm aquatic life.
Q3: How does wastewater treatment impact the environment?
A3: It reduces pollution, protects habitats, and helps maintain ecological balance.
Q4: Are there different methods of wastewater treatment?
A4: Yes, methods include physical, chemical, and biological treatments tailored to specific wastewater types.
Conclusion
Wastewater treatment is essential for maintaining public health, protecting the environment, and promoting sustainable water management. Investing in effective treatment systems benefits communities and ecosystems alike, ensuring a healthier future for all.