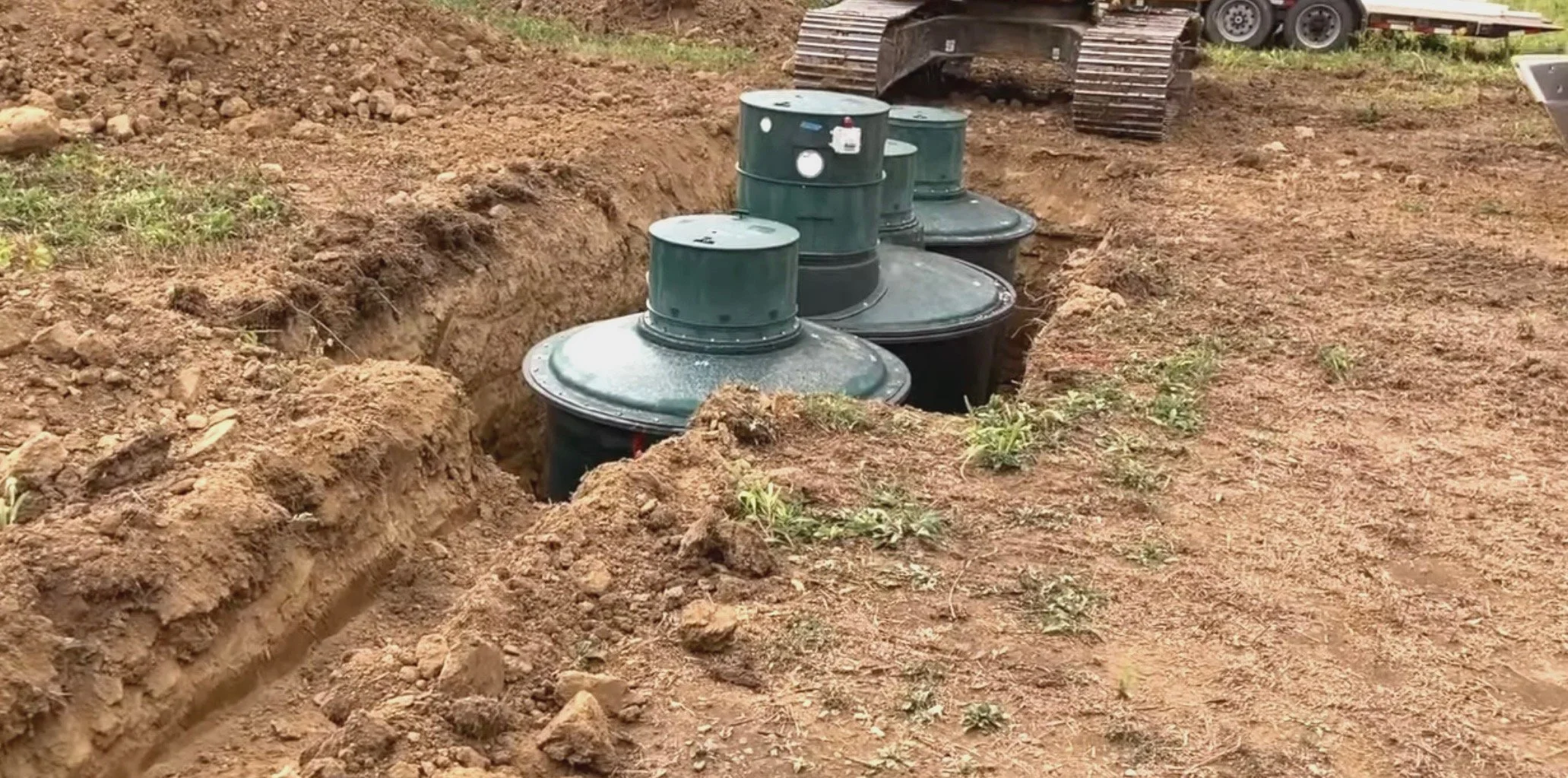
Septic Tank Installation in Sandy vs. Clay Soil
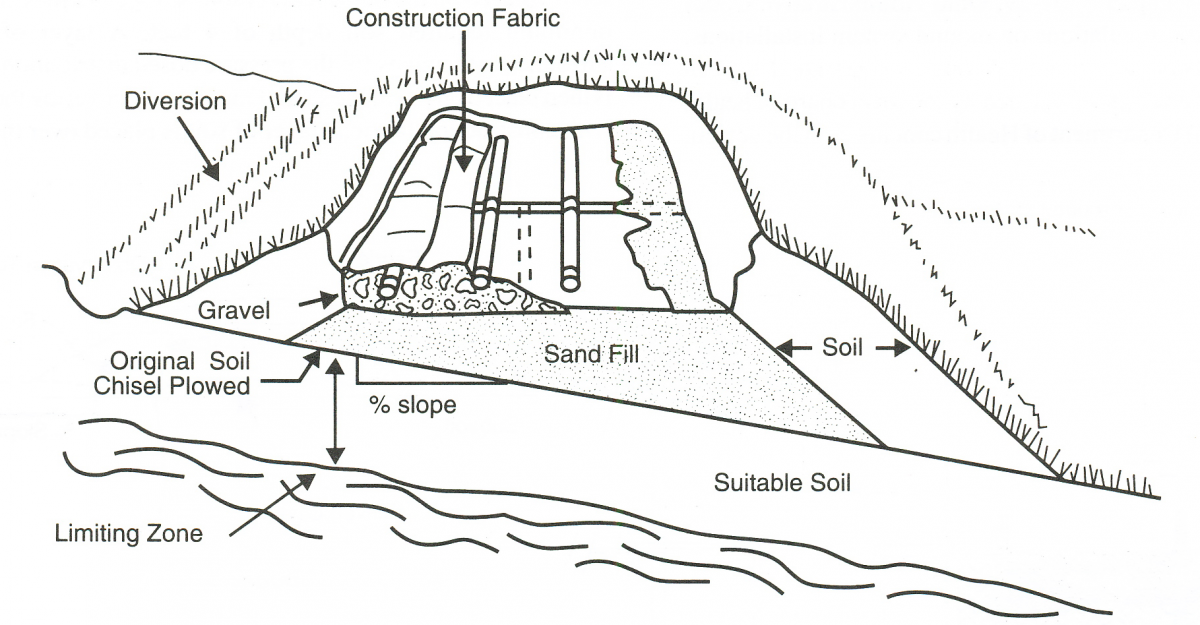
Installing a septic tank requires careful consideration of the soil type, as it significantly impacts the system’s efficiency, longevity, and environmental safety. Two common soil types encountered during installation are sandy soil and clay soil, each presenting unique challenges and benefits.
Understanding Soil Types
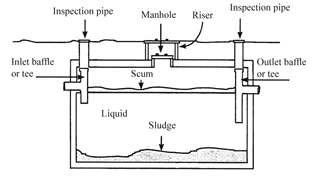
| Soil Type | Characteristics | Drainage Ability | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Loose, granular, large particles | Excellent drainage | Risk of rapid leachate flow, potential groundwater contamination |
| Clay Soil | Dense, fine particles, sticky when wet | Poor drainage | Slow percolation, risk of system backup and surface pooling |
Installation Considerations
Sandy Soil
- Drainage: Sandy soil’s high permeability allows wastewater to percolate quickly, which can be beneficial for absorption but may also lead to insufficient treatment time.
- Septic Tank Placement: Requires careful siting to prevent contamination of nearby groundwater sources due to rapid leachate movement.
- System Design: Often necessitates larger drain fields or additional filtration layers to ensure proper effluent treatment.
Clay Soil
- Drainage: Poor drainage means wastewater moves slowly, increasing the risk of system overload and surface water pooling.
- Septic Tank Placement: Must be positioned to avoid areas prone to waterlogging.
- System Design: May require enhanced drainage solutions such as raised drain fields or engineered sand layers to improve percolation.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Site Evaluation: Conduct soil testing to determine permeability and composition.
- System Design: Tailor the septic system based on soil characteristics.
- Excavation: Dig the tank and drain field areas according to design specifications.
- Tank Installation: Place the septic tank ensuring it is level and secure.
- Drain Field Installation: Install pipes and gravel beds, adapting to soil drainage properties.
- Backfilling and Testing: Cover the system and perform water tests to check for leaks or drainage issues.
Maintenance Tips for Different Soils
- Sandy Soil: Regularly inspect for signs of groundwater contamination; maintain vegetation to reduce erosion.
- Clay Soil: Monitor for surface pooling; avoid heavy machinery over drain fields to prevent compaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I install a septic tank in any soil type?
A: While septic tanks can be installed in most soils, the design and installation methods must be adapted to the soil’s drainage properties to ensure system effectiveness.
Q2: How does soil type affect septic tank lifespan?
A: Poor drainage in clay soils can cause system backups and damage, while sandy soils may risk contamination if not properly managed, both affecting lifespan.
Q3: What are the environmental risks of improper septic installation?
A: Risks include groundwater contamination, surface water pollution, and soil degradation, which can harm ecosystems and human health.
By understanding the differences between sandy and clay soils, homeowners and contractors can make informed decisions to optimize septic tank installation and maintenance, ensuring a safe and efficient wastewater management system.
