Septic Systems for Off-Grid Living: A Comprehensive Guide
Living off-grid offers freedom and sustainability, but it also requires self-sufficiency in managing waste. Septic systems are a crucial component for off-grid homes, providing an effective way to treat and dispose of wastewater without relying on municipal sewage systems. This article explores the essentials of septic systems tailored for off-grid living.
What is a Septic System?

A septic system is an underground wastewater treatment structure commonly used in rural areas without centralized sewer systems. It consists of three main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
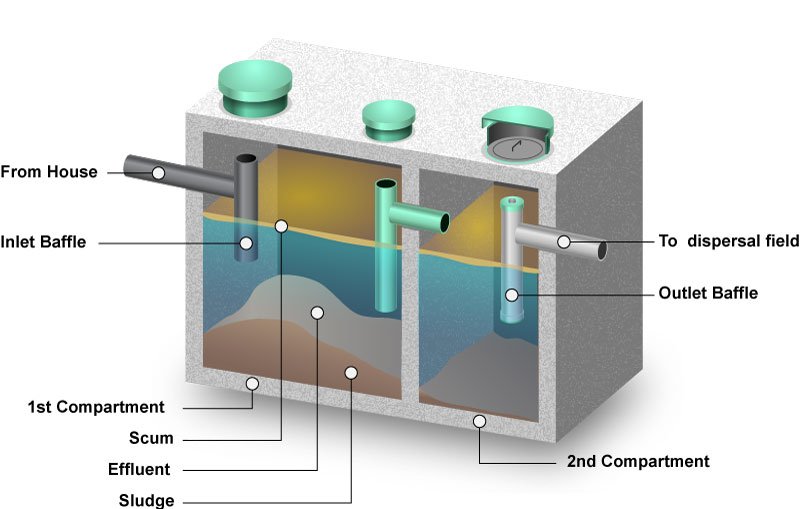
| Septic Tank | A watertight container that holds wastewater, allowing solids to settle and scum to float. |
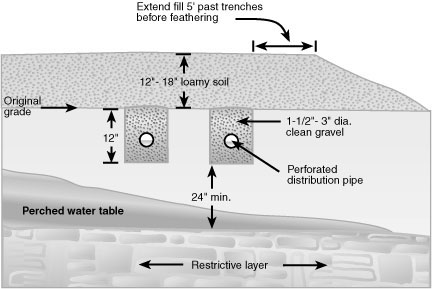
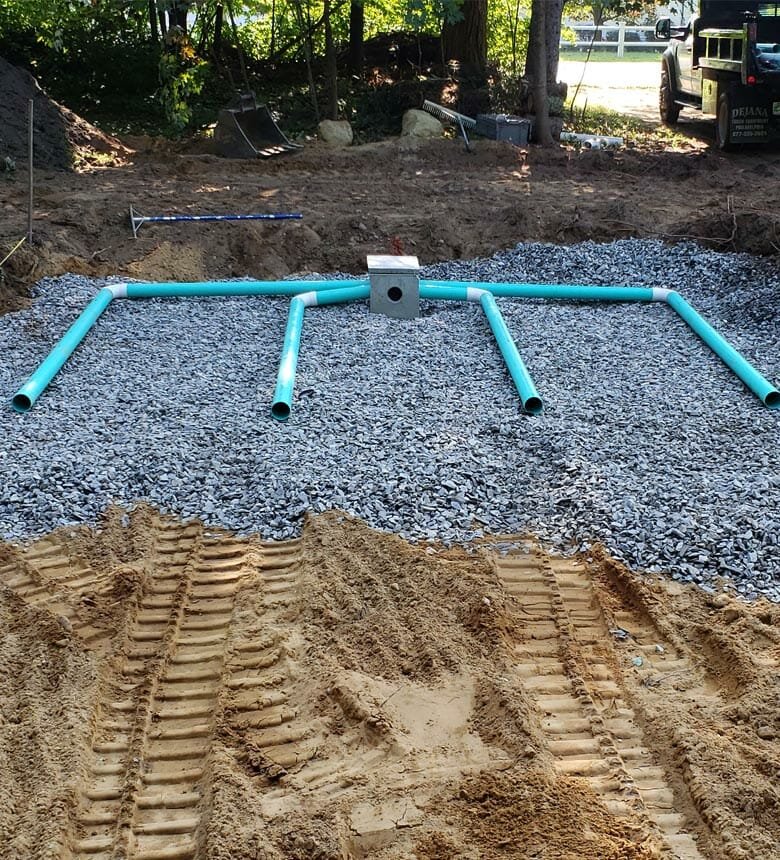
| Drainfield (Leach Field) | A network of perforated pipes buried in trenches that disperse the treated liquid into the soil. |
| Soil | Acts as a natural filter, removing harmful bacteria and nutrients from the wastewater. |
Why Use Septic Systems Off-Grid?
- Independence: Off-grid homes are not connected to municipal sewage, making septic systems essential.
- Cost-Effective: Installing a septic system can be more affordable than extending sewer lines.
- Environmental Benefits: Properly maintained septic systems minimize pollution and protect groundwater.
Types of Septic Systems Suitable for Off-Grid Living
- Conventional Gravity Systems: Use gravity to move wastewater from the tank to the drainfield.
- Pressure Distribution Systems: Use a pump to distribute wastewater evenly, ideal for uneven terrain.
- Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): Introduce oxygen to enhance bacterial breakdown, producing cleaner effluent.
- Composting Toilets: Reduce water use and produce compost, often paired with septic systems for greywater.
Designing a Septic System for Off-Grid Homes
Key considerations include:
- Soil Testing: Determines soil permeability and suitability for a drainfield.
- System Size: Based on household size and water usage.
- Location: Must comply with local regulations and avoid contamination of water sources.
- Maintenance Access: Ensure easy access for inspection and pumping.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
- Regularly inspect and pump the septic tank every 3-5 years.
- Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items.
- Conserve water to reduce system overload.
- Protect the drainfield from heavy vehicles and deep-rooted plants.
FAQ
Q1: How do I know if a septic system is right for my off-grid home?
A: If your property lacks access to municipal sewage, a septic system is typically the best solution.
Q2: Can I install a septic system myself?
A: Installation requires expertise and permits; professional installation is recommended.
Q3: What are the signs of septic system failure?
A: Slow drains, sewage odors, and wet spots near the drainfield indicate problems.
Q4: How much does a septic system cost?
A: Costs vary widely based on system type, size, and location but generally range from $3,000 to $10,000.
Conclusion
Septic systems are vital for sustainable off-grid living, offering an effective and environmentally friendly way to manage wastewater. Proper design, installation, and maintenance ensure a reliable system that supports your independent lifestyle.
For more detailed guidance, consult local regulations and professionals specializing in off-grid wastewater solutions.