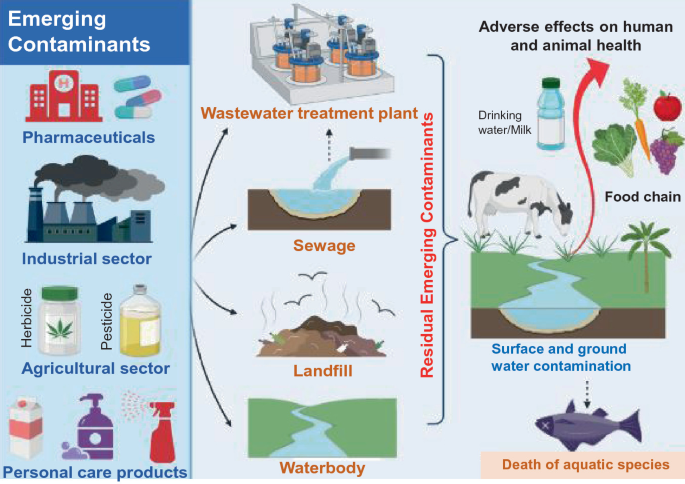
How Wastewater Affects the Environment

Wastewater, which includes sewage, industrial effluents, and stormwater runoff, plays a significant role in environmental health. Understanding its effects is crucial for developing sustainable water management practices.
Types of Wastewater

| Type | Source | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic Sewage | Households | Contains organic matter, pathogens |
| Industrial Waste | Factories and manufacturing | May contain toxic chemicals, heavy metals |
| Agricultural Runoff | Farms | Contains pesticides, fertilizers |
Environmental Impacts of Wastewater
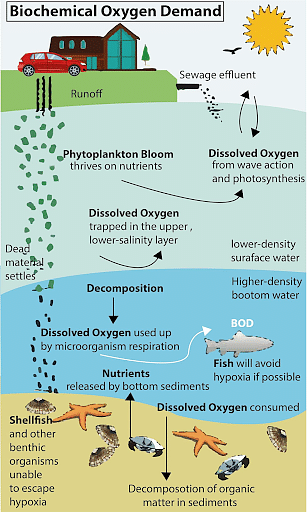
1. Water Pollution
Wastewater often contains harmful substances such as pathogens, nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), and toxic chemicals. When discharged untreated or inadequately treated into water bodies, it leads to:
- Eutrophication: Excess nutrients stimulate algal blooms that deplete oxygen, harming aquatic life.
- Contamination: Pathogens can cause waterborne diseases affecting humans and animals.
- Toxicity: Heavy metals and chemicals can accumulate in the food chain, impacting biodiversity.
2. Soil Contamination
Improper disposal of wastewater can lead to the accumulation of harmful substances in the soil, affecting soil fertility and potentially entering crops, which poses health risks to consumers.
3. Air Pollution
Certain wastewater treatment processes release gases like methane and hydrogen sulfide, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and unpleasant odors.
4. Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
Wastewater alters the physical and chemical properties of aquatic habitats, disrupting the balance of ecosystems. Sensitive species may decline or disappear, reducing biodiversity.
Wastewater Treatment and Mitigation
Effective treatment methods include:
- Primary Treatment: Removal of solids through sedimentation.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes to degrade organic matter.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced filtration and chemical treatments to remove nutrients and pathogens.
Implementing these treatments reduces environmental harm and protects public health.
FAQ
Q1: What happens if wastewater is not treated properly?
A: It can lead to severe water pollution, spread diseases, harm wildlife, and degrade ecosystems.
Q2: Can wastewater be reused?
A: Yes, treated wastewater can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and even replenishing groundwater.
Q3: How does agricultural runoff affect water bodies?
A: It introduces excess nutrients and pesticides, causing eutrophication and toxicity in aquatic environments.
Understanding the multifaceted impacts of wastewater on the environment highlights the importance of proper treatment and management to safeguard ecosystems and human health.