Fire Resistance in Fiberglass vs. Plastic Tanks

When selecting storage tanks for industrial or residential use, fire resistance is a critical factor to consider. Both fiberglass and plastic tanks offer unique advantages and challenges in terms of fire safety. This article explores the fire resistance properties of fiberglass and plastic tanks, helping you make an informed decision.
Understanding Fire Resistance

Fire resistance refers to a material’s ability to withstand fire or high temperatures without igniting, melting, or losing structural integrity. This property is crucial for tanks storing flammable or hazardous substances.
Fiberglass Tanks

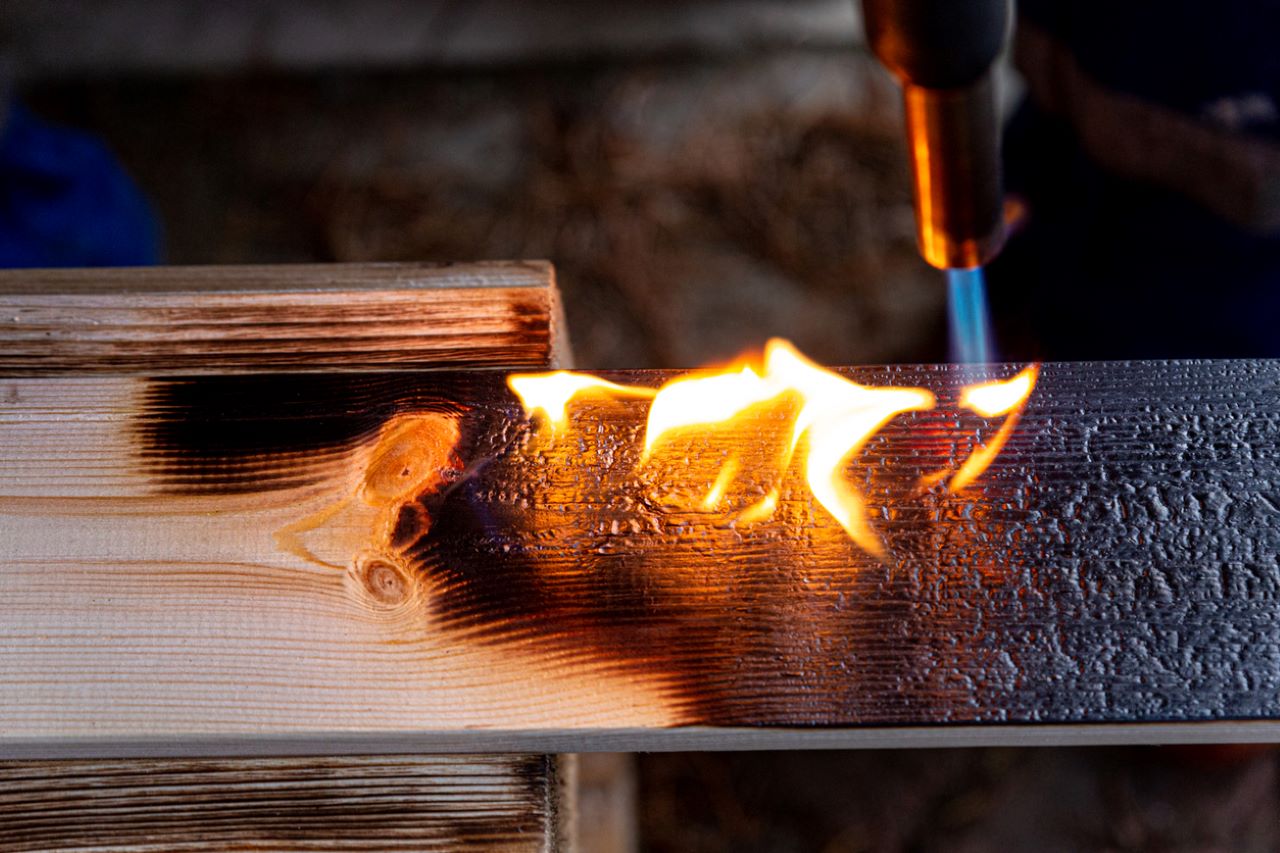
Fiberglass tanks are made from reinforced plastic materials combined with glass fibers, which enhance their strength and durability.
Fire Resistance Properties
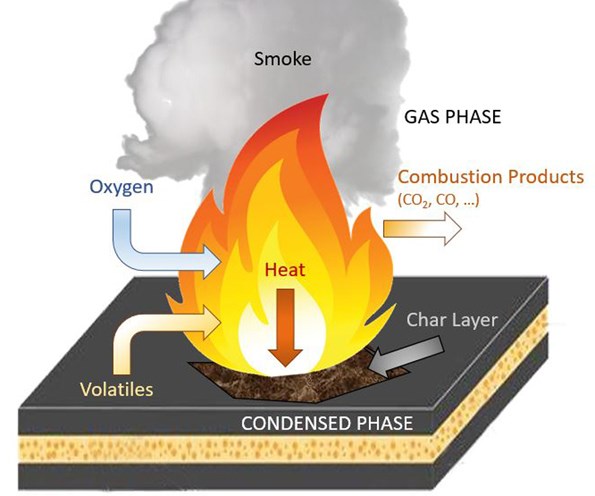
- High Heat Tolerance: Fiberglass can withstand higher temperatures before deforming compared to many plastics.
- Self-Extinguishing: Some fiberglass composites are treated with fire retardants, making them self-extinguishing when exposed to flames.
- Structural Integrity: Even under heat stress, fiberglass maintains its shape longer, reducing the risk of leaks or spills.
Advantages
- Resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
- Lightweight yet strong.
- Better fire resistance than many plastics.
Plastic Tanks
Plastic tanks are typically made from polyethylene, polypropylene, or PVC.
Fire Resistance Properties
- Lower Melting Points: Plastics generally melt or deform at lower temperatures.
- Flammability: Many plastics are combustible and can contribute to fire spread.
- Additives: Some plastic tanks include flame retardants, but effectiveness varies.
Advantages
- Cost-effective and widely available.
- Resistant to many chemicals.
- Lightweight and easy to install.
Comparative Table: Fiberglass vs. Plastic Tanks Fire Resistance
| Feature | Fiberglass Tanks | Plastic Tanks |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High (up to ~200°C or more) | Moderate to low (typically <100°C) |
| Flammability | Low (with fire retardants) | High (unless specially treated) |
| Structural Integrity | Maintains shape under heat | Deforms/melts quickly |
| Fire Retardant Additives | Commonly used | Sometimes used |
| Risk of Fire Spread | Lower | Higher |
FAQs
Q1: Can fiberglass tanks catch fire?
A1: While fiberglass is more fire-resistant than many plastics, it can still burn under extreme conditions, especially if not treated with fire retardants.
Q2: Are plastic tanks safe for storing flammable liquids?
A2: Plastic tanks can be used for flammable liquids but require careful consideration of the tank’s fire resistance rating and local safety regulations.
Q3: How can I improve the fire resistance of plastic tanks?
A3: Using tanks with flame retardant additives or installing external fire protection measures can enhance safety.
Conclusion
Choosing between fiberglass and plastic tanks depends on your specific needs, including fire safety requirements. Fiberglass tanks generally offer superior fire resistance, making them suitable for environments where fire risk is a concern. However, plastic tanks remain popular for their cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance, provided appropriate precautions are taken.
This detailed overview should help you understand the fire resistance differences between fiberglass and plastic tanks, aiding in safer and more informed tank selection.